How does it help you
The GitHub Enterprise integration enables us to provide reports that help you in:
- Daily stand-ups
- One-on-ones
- Code review
- Monthly and quarterly reports
For daily stand-ups, Waydev integrates with GitHub Enterprise to provide you with:
- Work Log, which displays a map of team contributions and work habits. Zoom in to all commits and pull requests an engineer produces, so you can make better decisions, set expectations proactively, and help your team improve over time.
- Daily Update, which helps you check the velocity of your team compared to the previous week. Find out where yesterday’s work focus went and if there were any engineers who didn’t check-in code. Direct your efforts to accomplish your goals.
- Time Card, which acts as a heatmap of your engineers’ activity, helping you see when are your engineers committing most. Set meetings in a nondisruptive manner – outside their peak productivity hours.
- Inactivity, which helps you achieve a healthy, continuous delivery workflow by making sure each of your engineers is involved in the development process.
For one-on-ones, Waydev integrates with GitHub Enterprise to help you with:
- Developer Summary, which provides valuable insights into each engineer’s output. Understand what your engineers’ work effectiveness is. Quickly spot and eliminate any blockers that are holding down your team.
- Developer Compare, which assists you with tracking your engineers’ progress. See how your engineers performed sprint over sprint. Understand their work dynamics and identify coaching opportunities.
- Developers Stats, which centralizes your engineers’ performance metrics. Aggregate all your engineers’ stats from Waydev in a highly customizable table. Sort, filter, search, and download to fulfill your needs.
For code review, Waydev integrates with GitHub Enterprise to provide you with:
- Review Workflow, which provides a map of pull request activity in the selected time frame. Identify long-running pull requests, unreviewed pull requests that have been merged, and spot closed pull requests that have not been merged.
- Review Collaboration, which presents a unified view of submitter and reviewer metrics of the PR process. Understand how your engineering teams work collaboratively. Effectively communicate the healthy tension between speed and thoroughness in code review.
- PR Resolution, which helps you identify the bottlenecks in your PR cycles over the course of the sprint. The PR resolution is designed to help you find outliers. Visualize high-level team dynamics and the underlying activities that can contribute to those dynamics.
- Submitter and Reviewer Fundamentals, which provide a view of how the metrics from the Review Collaboration evolved over time. These features should be used as a gauge to determine if your objectives regarding the code review workflow are on track.
For monthly and quarterly reports, Waydev integrates with GitHub Enterprise to help you with:
- Project Timeline, which provides a view of how work focus and volume modify over time. Find out where your engineers’ work focus is. View how events impacted your team’s performance and direct your data-driven decisions.
- Teams Stats, which provide a unified view of your teams’ engineering contribution. Gain a comprehensive view of all team stats from Waydev. Customize the report to your own requirements.
- Team Compare, which helps you track the progress of your engineering teams. See how engineering teams perform compared to the previous sprint, month, or quarter. View how work dynamics shift.
- Retrospective, which assists you in evaluating your release’s success and compare your sprints’ output.
- Repositories Stats, which provide clustered engineering stats to help you visualize performance from a repository point of view.
- Reports History, which encompasses weekly and monthly email reports into a singular view.
- Targets, which help you translate uncovered opportunities to action by setting measurable targets within the application. Visualize and track progress to hit all your goals.
How to integrate GitHub Enterprise into Waydev
Step 1: After you create a Waydev account, you will need to select a Git provider. Select GitHub Enterprise.
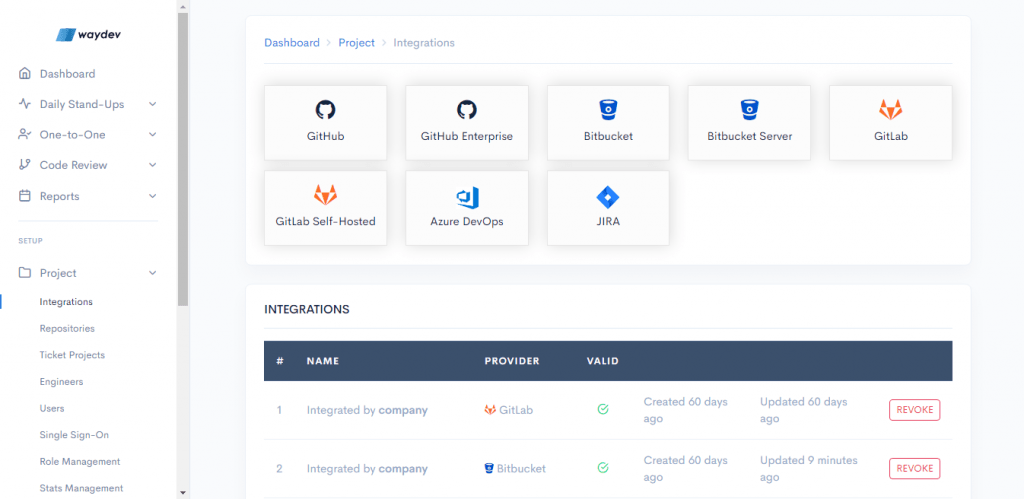
Step 2: Navigate to GitHub Enterprise and create an access token.
Step 3: In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
Step 4: In the left sidebar, click Developer settings.
Step 5: In the left sidebar, click Personal access tokens.
Step 6: Click Generate new token. Select the scopes, or permissions, you’d like to grant this token. To use your token to access repositories from the command line, select repo.
Step 7: Navigate back to Waydev and insert the following:
- Insert your GitHub Enterprise username
- Paste your Personal Access Token
- Insert your base URL in this format: https://github.yourcompany.com
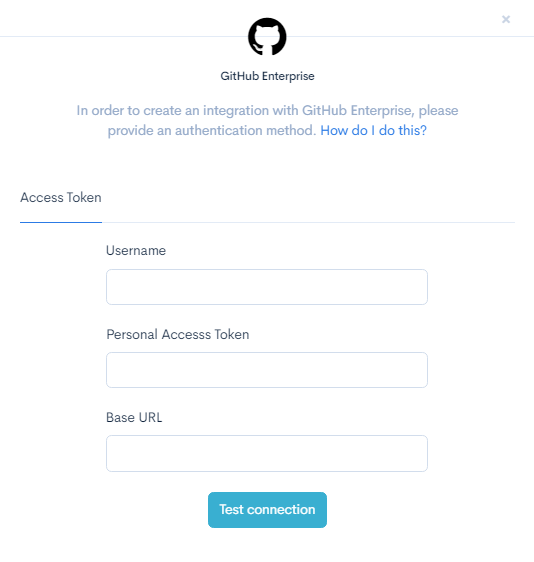
Step 8: You will be directed to the Repositories page, where you will need to select the repos you wish to import. After you select the repos, click Save Project. You have connected your GitHub Enterprise account successfully!
About GitHub Enterprise
GitHub Enterprise is the on-premises version of GitHub. GitHub Enterprise includes the same set of features as GitHub but it is packaged for running on your organization’s local network. All repository data is stored on machines that you control, and access is integrated with your organization’s authentication system (LDAP, SAML, or CAS).
GitHub Enterprise also includes support for pre-receive hooks, a tool that can help you enforce critical business rules, meet compliance requirements, and help prevent other undesired changes from ever being made. GitHub Enterprise is recommended when you need complete control over repository and project information.
Key terms
Three important terms used by developers in GitHub are fork, pull request, and merge. A fork, also known as a branch, is simply a repository that has been copied from one member’s account to another member’s account. Forks and branches allow a developer to make modifications without affecting the original code.
If the developer would like to share the modifications, they can send a pull request to the owner of the original repository. If, after reviewing the modifications, the original owner would like to pull the modifications into the repository, they can accept the modifications and merge them with the original repository. Commits are, by default, all retained and interleaved onto the master project, or can be combined into a simpler merge via commit squashing.
A repository is usually used to organize a single project. Repositories can contain folders and files, images, videos, spreadsheets, and data sets – anything your project needs.
Branching is the way to work on different versions of a repository at one time. By default your repository has one branch named master which is considered to be the definitive branch. We use branches to experiment and make edits before committing them to master.
When you create a branch off the master branch, you’re making a copy, or snapshot, of master as it was at that point in time. If someone else made changes to the master branch while you were working on your branch, you could pull in those updates.
In GitHub, saved changes are called commits. Each commit has an associated commit message, which is a description explaining why a particular change was made. Commit messages capture the history of your changes, so other contributors can understand what you’ve done and why.